When Life or Death Can Be a Matter of Minutes, Philly Doctors Are Turning To A.I. to Help Save More Lives
The implications of today’s artificial intelligence (AI) extend far beyond ChatGPT’s ability to sum up a quick email. When applied to essential human needs, as in the healthcare field, AI’s ability to rapidly process information can change, and even help save, lives.
Over the past few years, we’ve seen researchers and physicians unlock creative and transformational applications of AI, using it as everything from another set of eyes on medical imaging, to a tool that can help detect a wide array of health conditions.
One of the most exciting applications of AI is happening right here in Philadelphia, by the Pulmonary Embolism Response Team (PERT) at Temple Health, a care team whose work depends on efficiency and accuracy. Pulmonary embolism, a sudden blockage in the vessels that send blood to the lungs, creates an immediate and urgent crisis. For severe cases, in an instant, the world is spinning, your breathing is labored, your heart is pounding, and finding a fix for what’s going wrong with your body becomes your most imperative goal. Once physicians identify the obstruction in a patient, they’re in a race against time to determine and deliver appropriate treatment.
So it makes perfect sense that PERT physicians have found a way to combine the speed of artificial intelligence with a physician’s expertise and ingenuity to help them address the urgency of pulmonary embolism (PE) head on. Temple physicians have developed a powerful, standard-setting model for using FDA-approved artificial intelligence software as a kind of co-pilot for physicians to prioritize the most critical cases as soon as they’re screened by radiologists.
“I believe radiology is at the forefront of artificial intelligence in healthcare today, because there’s so much information to consider within one image,” says Dr. Gary Cohen, Chair and Professor of Radiology and Interventional Radiologist at Temple. “AI can point the finger, so to speak, and say, ‘That’s important; take a closer look here.’”
Through this pivotal innovation, the Temple Health team has shaved hours off the process to diagnose and treat, improving the quality of life after treatment, and saving more lives, for many of the hundreds of cases that regularly move through their health system. And as the team looks to the future, they’re finding new ways to make sure as many patients as possible can benefit from the full capabilities of this latest technological revolution.

Investigations in an Emergency
A pulmonary embolism is complex because of the number of factors that can go into the diagnosis. The embolism is typically identified through Computed Tomographic Angiography (CTA), but those images can be obscured from the movement of lungs breathing and the heart beating. And, since vessels in the lungs can be particularly small, details can be hard to see with the human eye. Each scan requires careful, comprehensive study, and hundreds of CTAs need to be reviewed each day.
Since time is of the essence, part of the medical team’s job is not just to make the right call, but to be able to rapidly identify the cases that need the most urgent help. To that end, the team segments patients by the severity of their risk: green representing relative safety; yellow representing that the patient is in danger of sliding into a near-deadly condition; and red, which acknowledges that the patient needs immediate intervention to avoid a fatal outcome.
This aspect of the diagnosis is just as important as identification of the blood clot, and is part of the reason why the process is so complex. As the body struggles and strains to circulate the blood in spite of the clot, patients are always at risk of rapidly moving from one phase to the next as the body begins to fail in that effort. Determining what parts of the body could fail at what rate is one reason why the patient’s complete health profile can play a part in determining the urgency of their clot.
An Innovative Approach to Prioritizing Care
With more than 60 deaths an hour nationally due to blood clots, physicians at Temple were motivated to find a better approach to treatment–one that could improve patient care all over the country.
That’s why they looked to take advantage of the growing AI revolution in health care. The artificial intelligence program that Temple implemented is connected to all CTAs that indicate the presence of a blood clot. The AI is set up to take into account the potentially thousands of relevant data points that determine how dangerous a person’s clot can be–and then distill that down to a value according to Temple’s green-yellow-red system.
Of course, pulling all that information together takes more than one physician, and that’s why Temple Health created PERT, designed to bring together a multidisciplinary team of physicians, including Dr. Cohen and pulmonologist Dr. Rali, to determine the right course of action once an embolism is detected. Dr. Rali not only serves as a Director of the Temple Health PERT program, but also serves as Chair of the Protocol Committee of the National PERT Consortium.
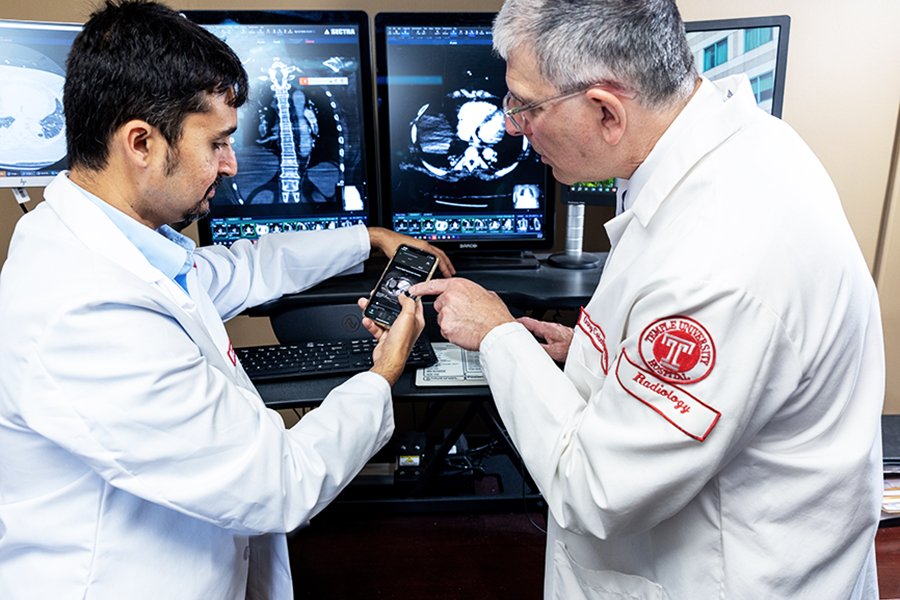
The AI software is connected to an app used by the entire team. As soon as the AI finds a patient at a critical juncture–say organ failure is about to send a patient from the yellow to the red phase–the AI notifies every physician on the team, giving them the opportunity to save the patient from a potential point of no return. Instead of waiting to gather the team together, the team can go directly to the images in the app to make decisions as a group–the AI even flags the most important points that led to its own diagnosis, for the physicians to examine first.
“This has added a level of comfort and collaboration beyond just the radiology detection. We can all be on this application, look at the clot, discuss it together, look at the images and the laboratory values together, and all discuss it at once,” Dr. Rali says. “I can’t tell you how much more quickly we can pull together a treatment plan that is quite complex, because you have many disciplines really involved in what that treatment plan should be.”
Perfecting the Process
Given that mere hours can make all the difference for many of these cases, the effect provided by the AI system, in terms of time to diagnosis, can be transformative.
“I think we have easily reduced the time to diagnosis by four to five hours in the care of these patients. I think that’s how impactful these technologies are,” Dr. Rali says.
But in addition to speeding up the diagnosis, the AI also acts as an important back up for the team in terms of making the right diagnosis. Small clots that are difficult to see, that may not even be the primary clot that is causing the current condition, can be more easily flagged with the assistance of the AI, for example.
That capability doesn’t just help with emergency diagnoses. Conditions picked up by the AI, like smaller, peripheral clots, can potentially have a larger effect on patients’ overall health and wellbeing over time than if left unchecked. The effect of those kinds of conditions are currently being studied by the Temple team with the help of artificial intelligence. Altogether, that means the proper use of AI could help them uncover a new understanding of how clotting impacts health on a more fundamental level.
“We’re very excited that we’re involved with AI, and we’re going to go deeper with it,” Dr. Cohen says. “And I think you’ll see exciting things to come for patients.”
This is a paid partnership between Temple Health and Philadelphia Magazine